Flask App deployment into Amazon EKS, using CICD Pipeline with Jenkins and Argo CD
Overview
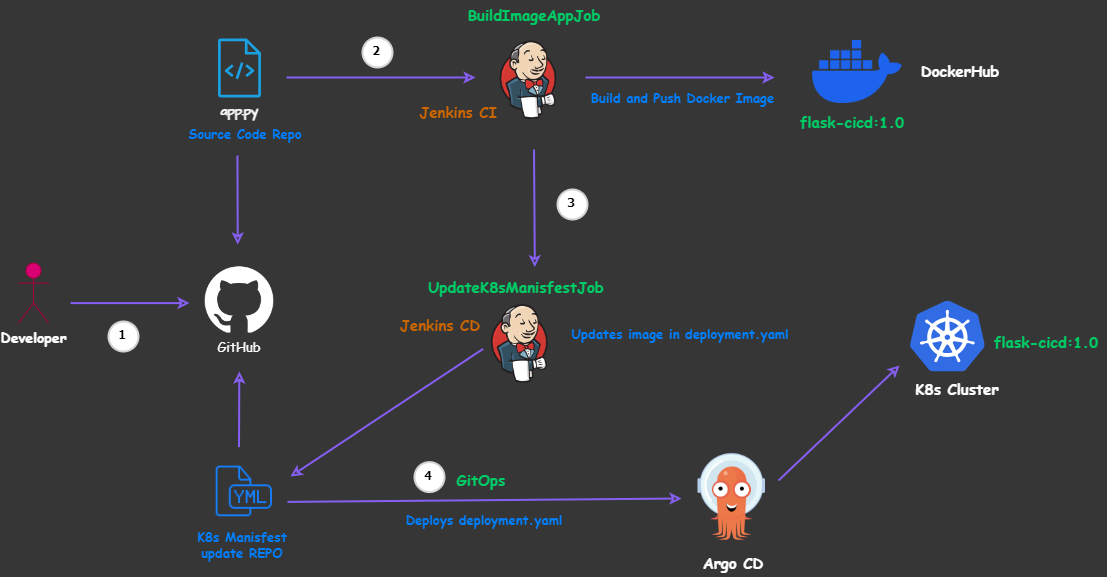
This project showcases an end-to-end DevOps pipeline for deploying a basic Flask application using Jenkins Pipeline and GitOps (with ArgoCD) on an Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (EKS) cluster. It utilises two Git repositories:
- GitHub Repository for Continous Integration hosting our basic Flask application code
- GitHub Repository for GitOps and Update of K8s Manifest
Pre-requisites/Assumptions:
- AWS Account created
- AWS CLI installed on local machine
- IAM user set up with AWS access key ID and AWS secret access key
- kubectl installed on local machine
- DockerHub Account created
- Application code hosted on GIT Repository
Architecture/Design Overview
Installation and Setup
1. Spin up an AWS EC2 instance for a Jenkins server:
Specs:
| Instance Type | OS | Storage | SG I/O Rules |
|---|---|---|---|
| t3.small | Ubuntu | 15 GiB gp2 | TCP/22, TCP/8080 |
-
SSH into your EC2 instance to install Jenkins and Docker packages.
-
Use the
user-datasection within the EC2 Console to incorporate the following bash script for installing Java, Jenkins, and Docker packages: -
Specs:
- Instance Type:
t3.small - OS:
Ubuntu - Storage:
15 GiB gp2 - SG Inbound rules:
TCP/22, TCP/8080
- Instance Type:
-
SSH into your EC2 instance to install Jenkins and Docker packages.
-
Use the
user-datasection within the EC2 Console to incorporate the following bash script for installing Java, Jenkins, and Docker packages:- Warning: Java 11 support in Jenkins ends after Sep 30, 2024. Installing an unsupported Java version may cause Jenkins to fail. Upgrade Java to a newer version. Refer to the documentation for details.
#!/bin/bash # Update and upgrade the system sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade -y # Install Java sudo apt install -y openjdk-11-jre # Install Jenkins curl -fsSL https://pkg.jenkins.io/debian/jenkins.io-2023.key | sudo gpg --dearmor -o /usr/share/keyrings/jenkins-keyring.gpg echo deb [signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/jenkins-keyring.gpg] https://pkg.jenkins.io/debian binary/ | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/jenkins.list > /dev/null sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get install -y jenkins # Install Docker sudo apt install -y docker.io # Grant Jenkins user permission to Docker daemon sudo usermod -aG docker jenkins sudo systemctl enable docker sudo systemctl restart docker -
SSH into your Jenkins EC2 instance and check status of packages by running the following commands:
java -versionsudo systemctl status jenkinssudo systemctl status docker
2. Configure Jenkins
- Install the necessary plugins by navigating to
Manage Jenkins > Plugins > Available Plugins - Choose
Docker,Docker PipelineandGitHub integration - Restart Jenkins server
- Configure Credentials:
Manage Jenkins > Credentials > Global > Add Credentials- for GitHub (
id=github, username=your_username, password=token_generated_in_GitHub) - for DockerHub (
id=dockerhub, username=your_username, password=your_dockerhub_pwd)
- for GitHub (
- Create 2 Jenkins Jobs:
- For CI Pipeline:
New Item > Name=BuildAppJob > Pipeline- Build Triggers=
GitHub hook trigger for GITScm polling - Navigate to the GitHub repository settings and enable the Webhook by following these steps:
Settings > Webhook > Payload URL=http://jenkins_server_public_ip:8080/github-weebhook/)Content type=application/json.- Confirm Add webhook
- Pipeline Definition=
Pipeline script from SCM- SCM=
GIT - Script Path=
Jenkinsfile - Repository URL=
https://github.com/Mik3asg/Flask_App_Jenkins_CI_EKS.git - Credentials=
none - Branch Specifier=
*/main
- SCM=
- Build Triggers=
- For CD Pipeline:
New Item > Name=UpdateK8sManifestJob > Pipeline- Select
This project is parameterized - String Parameter: Name=
DOCKERTAG, Default Value=latest - Pipeline Definition=
Pipeline script from SCM- SCM=
GIT - Script Path:
Jenkinsfile - Repo URL=
https://github.com/Mik3asg/Flask_App_Jenkins_GitOps_EKS.git - Credentials=
none# public repo - Branch Specifier=
*/main
- SCM=
- Select
- For CI Pipeline:
3. Provision AWS EKS Ckuster, through AWS CLI
-
Access your AWS Account via
aws configurein the Terminal of your local machine -
Provide the credentials of your IAM user (access key ID and secret key) and region
Note: For consistency, use the same region in which you have created your previous EC2 instance for Jenkins server, i.e. us-east-1
-
Create an AWS EKS Cluster
eksctl create cluster --name <flask-eks> --region us-east-1 --nodegroup-name <my-nodes> --node-type t3.small --managed --nodes 2 # Replace <flask-eks> and <my-nodes> with your desired values
- Check the status of EKS Cluster (if up and running)
eksctl get cluster --name demo-eks --region us-east-1
- Run
kubectl get nodescommand to verify the status of the nodes
4. Installation and Configuration of Argo CD
- Via CLI:
- Follow steps provided in the official Argo CD Documentation to:
-
Install Argo CD via CLI
-
Connect to the API server from local machine and access to UI using
https://localhost:8080Note: Keep the
kubectl port-forwardingterminal open to avoid disrupting access to the UI. Open a new terminal if you need CLI access. -
Retrieve Password for UI access
-
- Follow steps provided in the official Argo CD Documentation to:
- In UI:
- Application Name=
flask-gitops-demo - Project Name=
Default - SYNC POLICY=
Automatic - REPO URL:
<Github_repo_hosting_CD_Pipeline> - Path:
./ - Cluster URL=
https://kubernetes.default.svc - Namespace=
default
- Application Name=
5. Commit a new code change and test app deployment
- Check status in Jenkins UI of both Jobs:
BuildAppJobfor CI Pipeline andUpdateK8sManifestJobfor CD Pipeline - Check status of pods:
kubectl get pods - Check status in Argo CD UI

- Retrieve load balancer endpoint by running
kubectl get svc, then paste into web browser to access the web application
Clean-up resources
Delete AWS EKS Cluster
eksctl delete cluster --name flask-eks --region us-east-1 #Replace <flask-eks> with the value you defined for your cluster
Terminate the running EC2 instance for Jenkins server in AWS Console Management